Translate this page into:
A numerical performance of the novel fractional water pollution model through the Levenberg-Marquardt backpropagation method
⁎Corresponding author. salem.bensaid@uaeu.ac.ae (Salem Ben Said)
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
This article was originally published by Elsevier and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Peer review under responsibility of King Saud University.
Abstract
The aim of the current work is to provide the importance and significance of the fractional order (FO) derivatives for solving the nonlinear water pollution model (FWP) model. The FO derivative to solve the water pollution model is provided to get more precise results. The investigations through the non-integer and nonlinear mathematical form to define the fractional water pollution model are also provided in this study. The composition of the fractional water pollution model is classified into three classes, execution cost of control, system competence of industrial elements and a new diagnostics technical exclusion cost. The mathematical FWP system is numerically studied by using the artificial neural networks (ANNs) along with the Levenberg-Marquardt backpropagation method (ANNs-LMBM). Three different cases using the FO derivative have been examined to present the numerical performances of the FWP model. The data is selected to solve the mathematical FWP system is 70% for training and 15% for both certification and testing. The exactness of solver is observed through the comparison of the results. To ratify the aptitude, validity, constancy, and exactness of the ANNs-LMBM, the replications using the regression/correlation, state transitions, and error histograms are also described.
Keywords
Water pollution model
Artificial neural networks
Fractional order
Levenberg-Marquardt backpropagation
Nonlinear
Adams-Bashforth-Moulton
1 Introduction
The researcher’s community is taking keen interest for solving the nonlinear water pollution model (FWP) model due to the number of applications in industry. There are various investigations based on the supply chain are implemented between organizations to enhance the operational/financial concerns to decrease the catalogues and cost in the supply chain management (SCM) (Whang, 1995; Reyniers, 1992; Sox, 1997). The affiliating nature of inter-firm in the SCM is accessed by Mentzer et al (Mentzer, 2000). The manufacturing growing measure using the planned consequence of controlling, moderate design of SCM preparation than an illogical subsystems collection. The association between the industry groups is related to increase the shared prospect for these cultures with fine advantages (Mohr, 1994; Mentzer, 1999). The modeling procedures based on the SCM are presented by Min et al (Min, 2002) with various challenges, opportunities to model the systems of the supply chain.
The mathematical systems represent the numerous differential forms, e.g., SITR covid model (Owolabi and Atangana, 2019), dengue virus model (Heydari and Atangana, 2019), nervous stomach model (Solís-Pérez et al., 2018), vector disease model (Parsamanesh and Erfanian, 2021) and mosquito dispersal model (Gao et al., 2021). To predict the unified growth, the growing rate of the low economy does not unstable with prominent world’s economies of the world faced troubles using the economic disaster. The design of “predator-victim” model that presents the authorizations of the model to describe their reports. The mathematical presentations of the FWP model have three classes, new procedural diagnostics, and cost of control principles (X), disasters exclusion costs (Y) and system’s capability of industry essentials (Z). The mathematical structure to express these quantities is provided as (Meena and Kishor, 2021; García-Farieta and Casas-Miranda, 2018; Atangana and Araz, 2021):
The system (1) is known as fractional order (FO) derivatives in the FWP model, i.e., FWP model, where, K1, K2,….…, K8 are the constant coefficients. The initial conditions are represented as l1, l2 and l3. The purpose of this study indicates the importance and significance of FWP model based on the procedure of artificial neural networks (ANNs) and the Levenberg-Marquardt backpropagation method (ANNs-LMBM). The extended form of the FWP model is given as:
Where, represents the FWP model, the Caputo operator is used as a fractional order derivative in this study. The fractional order derivatives have been taken between 0 and 1. The integer order derivative has already been used to solve this nonlinear system. However, these derivatives are used in this study to achieve more realistic performances for solving the nonlinear FWP model.
The other parts are provided as: The summary of the stochastic solvers is given in Sect 2. The proposed ANNs-LMBM is described in Sect 3. The simulations of the FWP model are narrated in Sect 4. Conclusions are provided in the last Sect.
2 Novel aspects and stochastic applications
In this section, the stochastic solvers based on ANNs-LMBM are derived to solve the FO form of the derivative using the FWP model. The stochastic solvers have been tested by using the local and global operator performances in order to solve a number of nonlinear, singular and complicated differential models. Some of the eminent stochastic applications are COVID-19 systems (Owolabi et al., 2021; Umar, 2021), fractional order models (Sabir et al., 2021; Sabir et al., 2021), functional order system (Guirao et al., 2020), periodic differential system (Wang et al., 2022), third kind of nonlinear singular system (Signing et al., 2022) and delay model (Zhou et al., 2021).
These investigations provide the numerical investigations of FO model of FWP by using the stochastic performances of the ANNs-LMB. The integer order shows remembrance, whereas the memory function represents the form of FO. The FO form is applied to the application of the real-world systems (Yokuş and Gülbahar, 2019; Sulaiman et al., 2019; İlhan and Kıymaz, 2020; Akdemir et al., 2021; Durur et al., 2020; Heydari and Atangana, 2019; Atangana and Araz, 2021; Owolabi and Atangana, 2019; Haq, 2022; Bukhari et al., 2022). Few novel investigations of this work are provided as:
-
A design of fractional order water pollution model is presented and numerically solved successfully.
-
The numerical performances based on the stochastic solvers are not applied to solve the FWP model.
-
The solutions of the mathematical nonlinear FWP model have been successfully presented by using the stochastic ANNs-LMBM.
-
Three FO derivative cases have been examined to signify the numerical presentations of the mathematical FWP model.
-
The brilliance of the stochastic ANNs-LMBM procedures is accomplished via the comparison of reference (Adam solutions) and calculated solutions.
-
The absolute error (AE) performances with the matching of order 4 to 6 is performed to solve the mathematical FWP model.
-
The reliability and constancy of the proposed ANNs-LMBM is tested using the error histograms (EHs), correlation, state transitions (STs), mean square error (MSE) and regression to solve the mathematical FWP model.
3 Designed scheme: ANNs-LMBM
In this section, the ANNs-LMBM structure is accessible to solve the mathematical FWP model. The methodology is divided in two phases: the essential procedures using the ANNs-LMBM are provided, while the execution method via designed procedures is described to solve the mathematical FWP model. Fig. 1 indicates the multi-layer optimization performance using the stochastic ANNs-LMBM. Whereas the single layer neuron structure is provided in Fig. 2. The data is selected to solve the FWP model as 70 % for training and 15 % for both authorization and testing.
Workflow structure for solving the mathematical FWP model.
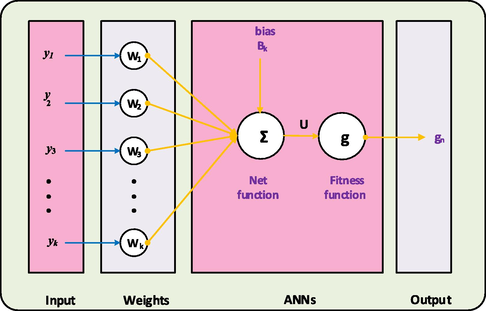
A single layer structure.
The parameter setting based on the stochastic structure is presented for the FWP model is shown in Table 1.
Index
Settings
Hidden layer of neurons
15
Increasing mu values
10
Fitness
0
Authentication fail amount
6
Epochs
900
Adaptive mu parameter
5 × 10-03
Maximum Mu values
1010
Decreeing mu values
0.1
Minimum gradient
10-07
Test data
15 %
Validation data
15 %
Train data
70 %
Sample selection
Random
Hidden/output layers
Single
Dataset generation
Adam
Reference solutions
Default
4 Results and simulations
This section presents three FO variations to solve the mathematical FWP model. The fractional order derivative has been studied in various applications like as chaotic fractional Rossler system (Ahmad et al., 2022), leakage delay (Alzabut et al., 2020), fractional q-integro-differential equations (Hajiseyedazizi et al., 2021), COVID-19 disease model (Arfan et al., 2022; Javeed et al., 2021), Kundu-Eckhaus equation and massive thirring model (Wang et al., 2022) and tumor invasion and metastasis (Veeresha et al., 2021), fractional dengue model (Ahmad et al., 2021) and tuberculosis model (Zafar et al., 2022).
Consider the mathematical FWP model by taking the suitable parameter values along with
is given as:
Consider the mathematical FWP model with the appropriate values along with
is given as:
Consider the mathematical FWP model with
is given as:
The numerical simulations of the FWP model are presented using the ANNs-LMBM with 15 numbers of neurons together with the selection of data to solve the FWP network is executed as 70 % for training and both testing, and certification are 15 %. The input, hidden and output layers structure with 15 neurons are plotted in Fig. 3.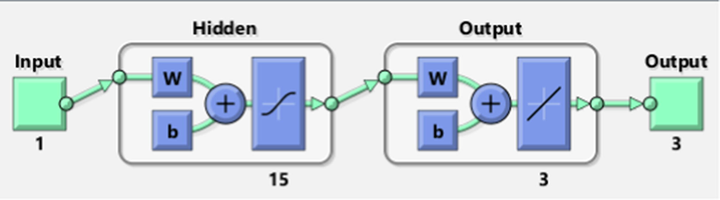
Proposed LMBS-NNs structure for the mathematical FWP model.
Figs. 4-8 indicate the graphical illustrations for the mathematical FWP model based stochastic structure of ANNs-LMB. The graphical representations are provided in the plots 4 and 5 in order to show the STs and the best performances. The MSE and STs based on the best curves, training and verification are provided in Fig. 4 for the mathematical FWP model. The best performances of the solver for the mathematical FWP model have been plotted at epochs 81, 813 and 850, which are 1.1158 × 10–04, 1.3409 × 10–10 and 2.2393 × 10–10. The gradient is calculated at 4.1547 × 10-03, 9.9851 × 10-08 and 9.8482 × 10-08. These illustrations show the convergence of the proposed ANNs-LMB for the mathematical FWP model. The fitting curves are provided in Fig. 5 for the mathematical FWP model. The error illustrations have been drawn through the training, testing and authentication to solve each case of the mathematical FWP model using the ANNs-LMBM procedures. The EHs plots are provided in Fig. 5(a-c), while the regression plots are drawn in Fig. 5(d-f) to solve the mathematical FWP model. The EHs are calculated as 3.24 × 10-04, 9.21 × 10-06 and 8.04 × 10-06 for case 1–3. The correlation is shown in Fig. 6 to demonstrate the regression performance. One can observe that the correlation values are 1, which shows the perfect modelling. The testing/ verification/training measures label the correctness of the ANNs-LMBM procedure for the mathematical FWP model. The MSE convergence is observed to check the complexity measures, training, iterations, backpropagation, testing and validation, which is provided in Table 1 to solve the mathematical FWP model (see Table 2).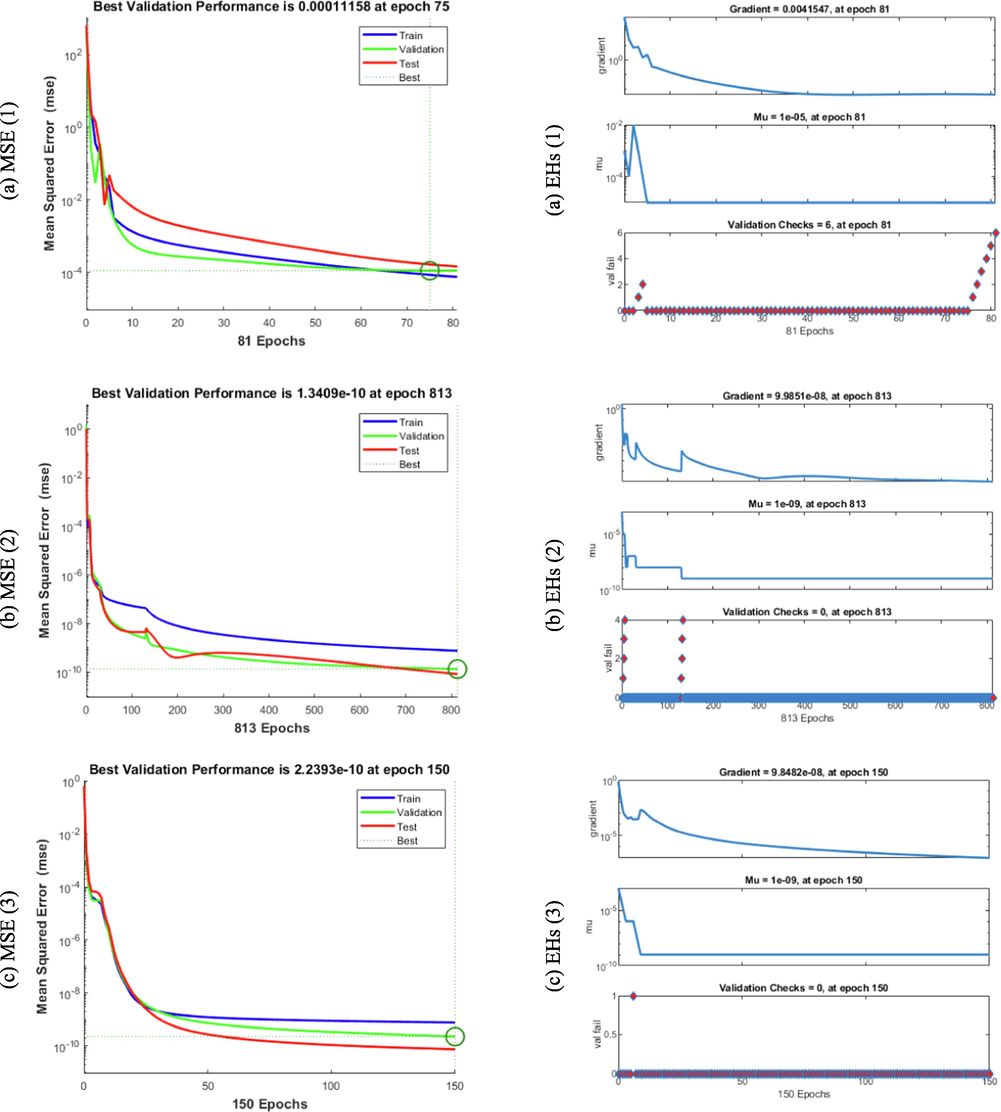
STs and MSE for the mathematical FWP system.
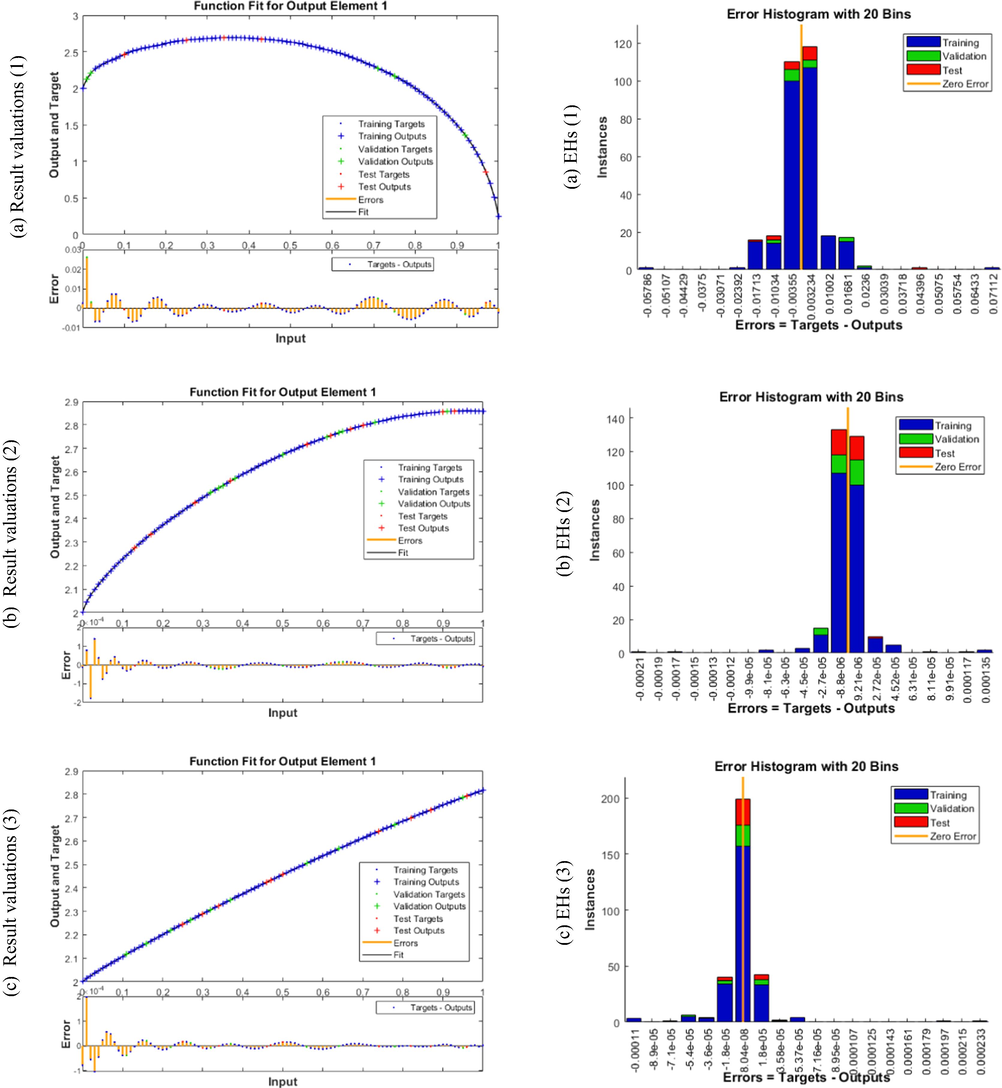
Results valuations and EHs for the mathematical FWP system.
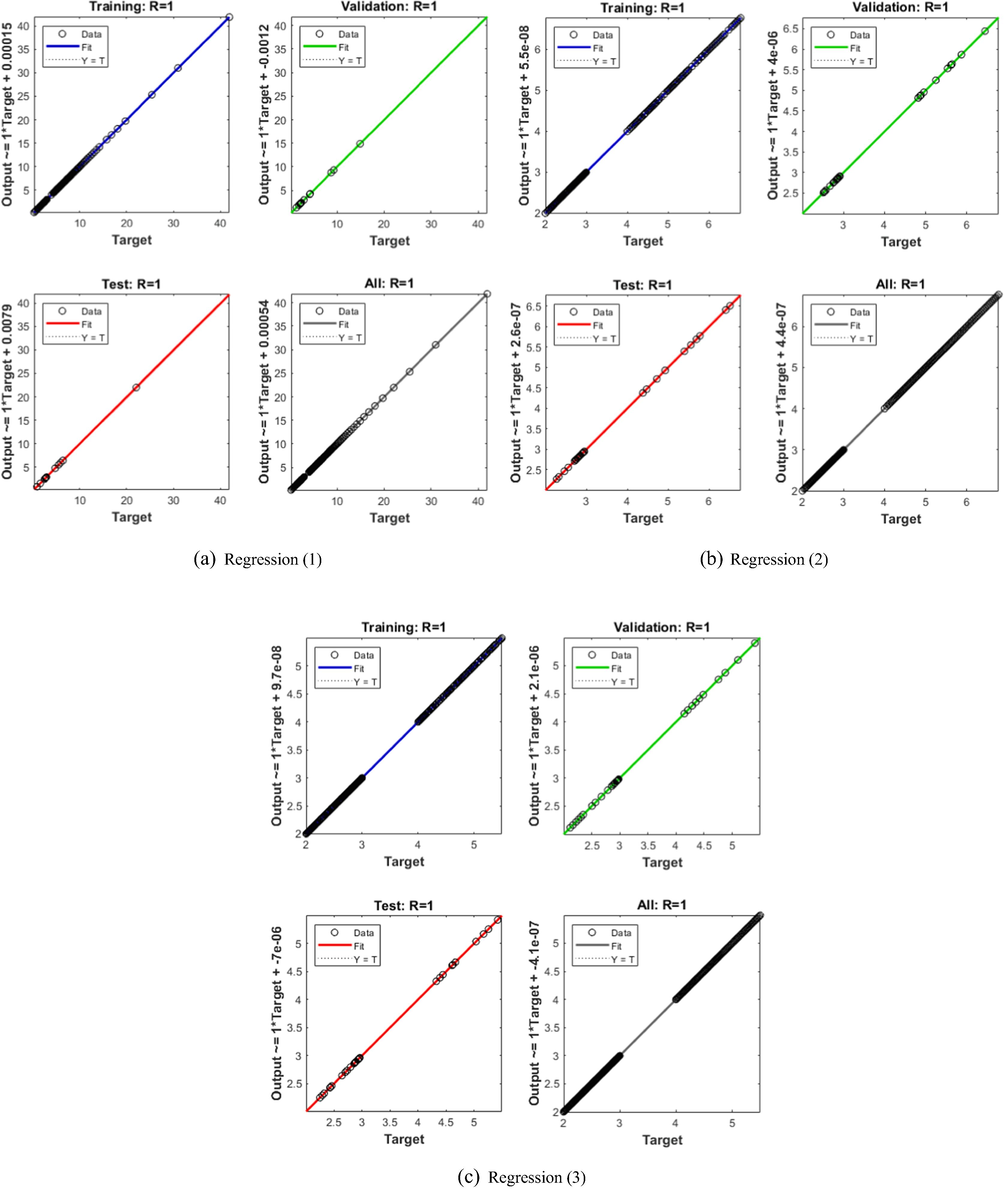
Regression plots for the FWP system.
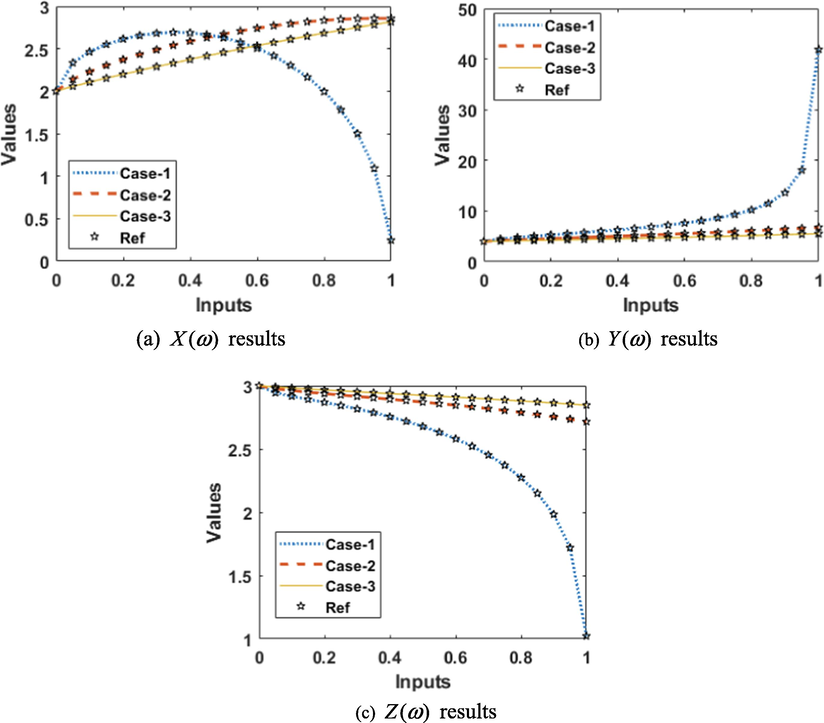
Result for the mathematical FWP system.
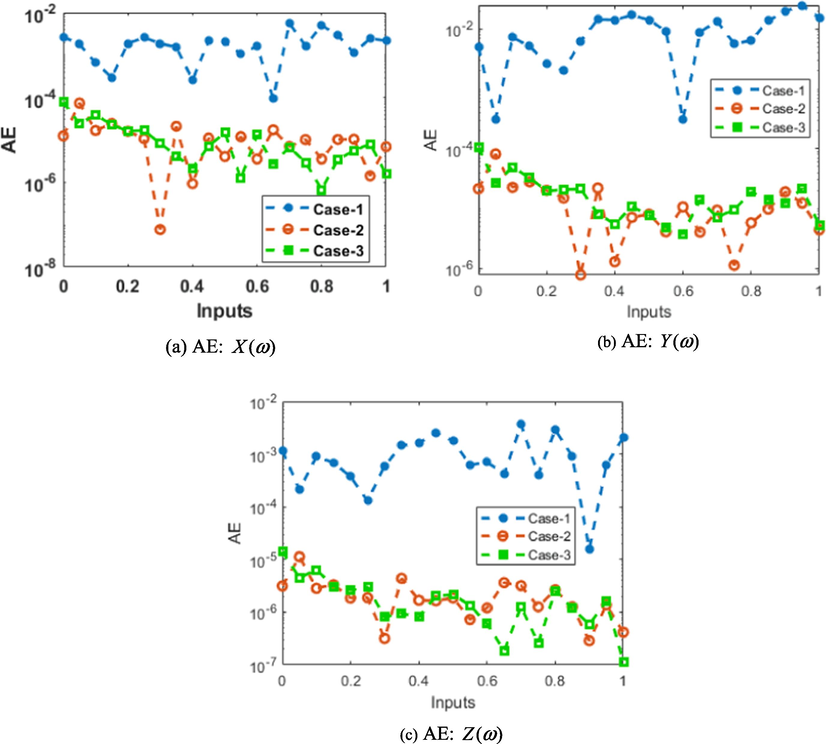
AE for the mathematical FWP system.
Case
MSE
Gradient
Performance
Epoch
Mu
Time
Training
Testing
Validation
1
8.56 × 10-05
1.67 × 10-04
1.11 × 10-04
0.001 × 10-05
7.52 × 10-05
81
1 × 10-05
2 Sec
2
7.62 × 10-10
8.44 × 10-11
1.34 × 10-10
9.99 × 10-08
7.63 × 10-10
813
1 × 10-09
5 Sec
3
7.65 × 10-10
7.45 × 10-11
2.23 × 10-10
9.85 × 10-08
7.66 × 10-10
150
1 × 10-09
3 Sec
The comparison performances through the results overlapping along with the AE values have been performed for the mathematical FWP system is provided in Figs. 7 and 8. The numerical representations for each class of the mathematical FWP system have been provided using the stochastic procedures based on the ANNs-LMBM. The depiction of proposed and reference solutions is provided in Fig. 7, which represents in the form of overlapping of the results. These overlapped performances authenticate the exactness of ANNs-LMBM. The performances of the AE are provided in Fig. 8 for the FWP system. The AE for found around 10-02 to 10-04, 10-04 to 10-06 and 10-04 to 10-08 for case 1 to 3 for the FWP model. The AE for is calculate as 10-02 to 10-04 for case 1, 10-04 to 10-06 for case 2 and 3 for the mathematical FWP model. The AE for found 10-03 to 10-05 for case 1, 10-05 to 10-07 for case 2 and 3 for the mathematical FWP model. These good performances of the AE show the exactness of the ANNs-LMB-NNs to solve the mathematical FWP model.
5 Concluding remarks
The purpose of this work is to introduce a stochastic numerical procedure for solving a class of fractional order derivatives of the nonlinear water pollution model. The dynamics of the nonlinear water pollution model become more accurate and precise with the involvement of the fractional order derivative. The composition of FWP model is classified into three classes, execution cost of control, system competence of industrial elements and a new diagnostics technical exclusion cost. The dynamics of the fractional order FWP model has never been tested before through the stochastic solvers. The artificial neural networks along with the Levenberg-Marquardt backpropagation method have been presented for the FWP model. Three different cases using the FO derivative have been examined for the numerical outputs of the FWP model. The data selection for the mathematical FWP is executed as 70 % for training and 15 % for both testing and certification. Fifteen neurons are used to solve the mathematical FWP system throughout this study and the obtained measures are compared with the reference Adams method. To reduce the MSE performances that the numerical results have been performed through ANNs-LMBM. The negligible AE performances also indicate the exactness of the scheme. To authorize the aptitude, reliability, and capability of the ANNs-LMBM, the numerical simulations have been performed through EHs, STs, correlation and regression. The accuracy of ANNs-LMBM is observed to solve the mathematical FWP system via overlapping of the proposed and reference outcomes. Moreover, the performance is indicated to authenticate the dependability of the scheme.
In future studies, the LMB-NNs approaches have been used to solve the numerical performance of the nonlinear models based on the Liénard Differential Model (Yan et al., 2023), fiber optic communication (Yokus and Baskonus, 2022), food chain model (Sabir, 2022) and thermal explosion theory (Sabir, 2022; Sabir et al., 2022).
Conflict of interest
All authors describe that there are no potential conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to UAEU for the financial support through the UPAR grant number 12S002.
References
- Analysis and numerical solution of novel fractional model for dengue. Results Phys.. 2021;28:104669
- [Google Scholar]
- Fractional order model for the coronavirus (COVID-19) in Wuhan. China. Fractals. 2022;30(01):2240007.
- [Google Scholar]
- On some integral inequalities via conformable fractional integrals. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences. 2021;6(1):489-498.
- [Google Scholar]
- Discrete fractional-order BAM neural networks with leakage delay: existence and stability results. Asian J. Control. 2020;22(1):143-155.
- [Google Scholar]
- On nonlinear dynamics of COVID-19 disease model corresponding to nonsingular fractional order derivative. Med. Biol. Eng. Compu.. 2022;60(11):3169-3185.
- [Google Scholar]
- New concept in calculus: Piecewise differential and integral operators. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021;145:110638
- [Google Scholar]
- Design of intelligent computing networks for nonlinear chaotic fractional Rossler system. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2022;157:111985
- [Google Scholar]
- New analytical solutions of conformable time fractional bad and good modified Boussinesq equations. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences. 2020;5(1):447-454.
- [Google Scholar]
- Oceanic studies via a variable-coefficient nonlinear dispersivewave system in the Solar System. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021;142 p. 110367. 57
- [Google Scholar]
- Effect of observational holes in fractal analysis of galaxy survey masks. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2018;111:128-137. 59
- [Google Scholar]
- Guirao, J.L., et al., 2020. Design and numerical solutions of a novel third-order nonlinear Emden–Fowler delay differential model. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020.
- On multi-step methods for singular fractional q-integro-differential equations. Open Mathematics. 2021;19(1):1378-1405.
- [Google Scholar]
- Partial-approximate controllability of semi-linear systems involving two Riemann-Liouville fractional derivatives. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2022;157:111923
- [Google Scholar]
- A cardinal approach for nonlinear variable-order time fractional Schrödinger equation defined by Atangana–Baleanu–Caputo derivative. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2019;128:339-348. 63
- [Google Scholar]
- A generalization of truncated M-fractional derivative and applications to fractional differential equations. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences. 2020;5(1):171-188.
- [Google Scholar]
- A novel mathematical model for COVID-19 with remedial strategies. Results Phys.. 2021;27:104248
- [Google Scholar]
- First order stability test of equilibrium points in the planar elliptic restricted four body problem with radiating primaries. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021;150 p. 111138. 58
- [Google Scholar]
- Two heads are better than one if your company spans the globe. Acad. Manag. Perspect.. 1999;13(2):89-90.
- [Google Scholar]
- The nature of interfirm partnering in supply chain management. J. Retail.. 2000;76(4):549-568.
- [Google Scholar]
- Supply chain modeling: Past, present and future. Computers and Industrial EngiFWPring. 2002;43:231-249.
- [Google Scholar]
- Characteristics of partnership success: partnership attributes, communication behavior, and conflict resolution techniques. Strateg. Manag. J.. 1994;15(2):135-152.
- [Google Scholar]
- Mathematical analysis and computational experiments for an epidemic system with nonlocal and nonsingular derivative. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2019;126:41-49. 47
- [Google Scholar]
- Analysis and pattern formation scenarios in the superdiffusive system of predation described with Caputo operator. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021;152:111468
- [Google Scholar]
- Stability and bifurcations in a discrete-time SIVS model with saturated incidence rate. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021;150 p. 111178. 56
- [Google Scholar]
- Supplier-customer interaction in quality control. Ann. Oper. Res.. 1992;34(1):307-330.
- [Google Scholar]
- Neuron analysis through the swarming procedures for the singular two-point boundary value problems arising in the theory of thermal explosion. The European Physical Journal Plus. 2022;137(5):638.
- [Google Scholar]
- Stochastic numerical investigations for nonlinear three-species food chain system. Int. J. Biomath.. 2022;15(04):2250005.
- [Google Scholar]
- Solution of novel multi-fractional multi-singular Lane-Emden model using the designed FMNEICS. Neural Comput. & Applic.. 2021;33(24):17287-17302.
- [Google Scholar]
- Meyer wavelet neural networks to solve a novel design of fractional order pantograph Lane-Emden differential model. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021;152:111404
- [Google Scholar]
- Neuron analysis of the two-point singular boundary value problems arising in the thermal explosion’s theory. Neural Process. Lett. 2022:1-28.
- [Google Scholar]
- A cryptosystem based on a chameleon chaotic system and dynamic DNA coding. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2022;155:111777
- [Google Scholar]
- Novel numerical method for solving variable-order fractional differential equations with power, exponential and MittagLeffler laws. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2018;114:175-185.
- [Google Scholar]
- Coordinating production and inventory to improve service. Manag. Sci.. 1997;43(9):1189-1197.
- [Google Scholar]
- Optical solitons to the fractional Schrdinger-Hirota equation. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences. 2019;4(2):535-542.
- [Google Scholar]
- Integrated neuro-swarm heuristic with interior-point for nonlinear SITR model for dynamics of novel COVID-19. Alex. Eng. J.. 2021;60(3):2811-2824.
- [Google Scholar]
- Regarding on the Fractional Mathematical Model of Tumour Invasion and Metastasis. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci.. 2021;127(3):1013-1036.
- [Google Scholar]
- Regarding deeper properties of the fractional order Kundu-Eckhaus equation and massive thirring model. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci.. 2022;133(3):697-717.
- [Google Scholar]
- Practical finite difference method for solving multi-dimensional black-Scholes model in fractal market. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2022;157:111895
- [Google Scholar]
- Design of a Computational Heuristic to Solve the Nonlinear Liénard Differential Model: Nonlinear Liénard Differential Model. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci.. 2023;1–12
- [Google Scholar]
- Dynamics of traveling wave solutions arising in fiber optic communication of some nonlinear models. Soft. Comput. 2022
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Numerical solutions with linearization techniques of the fractional Harry Dym equation. Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Sciences. 2019;4(1):35-42.
- [Google Scholar]
- Analysis and numerical simulation of tuberculosis model using different fractional derivatives. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals; 2022.
- Gene essentiality prediction based on chaos game representation and spiking neural networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2021;144:110649
- [Google Scholar]







